|
|
Precision Cutting
Precision wafer cutting is most commonly accomplished with diamond wafering blades, however for some materials the use of cubic boron nitride (CBN) is the more effiicient wafering blade. In addition, optimal wafer cutting is accomplished with by maximizing the abrasive concentration and abrasive size, as well as b choosing the most appropriate cutting speed and load. The following table provides the recommended parameters for precision wafering sectioning.
WAFER BLADE SELECTION GUIDELINES
Material |
Characteristic |
Speed (rpm) |
Load (grams) |
Blade (grit/conc.) |
Silicon substrate |
soft/brittle |
<300 |
<100 |
Fine/low |
Gallium arsenide |
soft/brittle |
<200 |
<100 |
Fine/low |
Boron composites |
very brittle |
500 |
250 |
Fine/low |
Ceramic fiber composites |
very brittle |
1000 |
500 |
Fine/low |
Glasses |
brittle |
1000 |
500 |
Fine/low |
Minerals |
friable/brittle |
>1500 |
>500 |
Fine/low |
Alumina ceramic |
hard/tough |
>1500 |
>500 |
Medium / low |
Zirconia (PSZ) |
hard/tough |
>3500 |
>800 |
Medium/low |
Silicon nitride |
hard/tough |
>3500 |
>800 |
Medium/low |
Metal matrix composites |
|
>3500 |
>500 |
Medium/high |
General purpose |
|
variable |
Variable |
Medium/high |
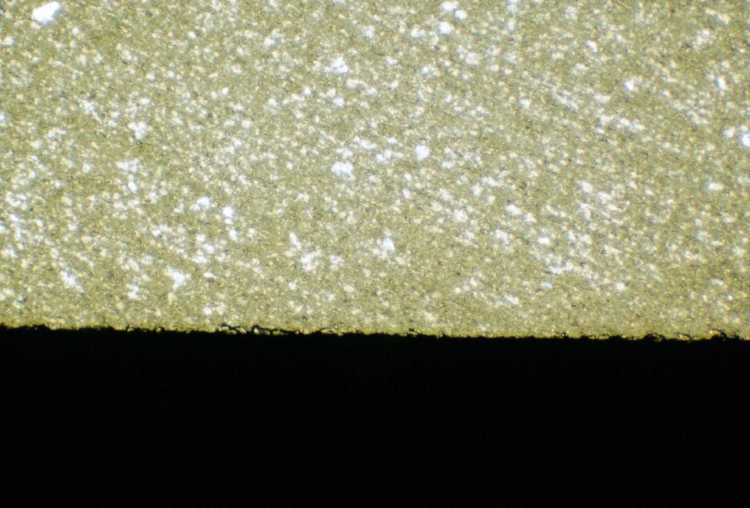
Perhaps the most important parameter for diamond sectioning is the abrasive size. Similar to grinding and polishing, finer abrasives produce less damage. For extremely brittle materials, finer abrasives are required to minimize and manage the damage produced during sectioning. Sectioning with a fine abrasive wafering blade is often the only way that a specimen can be cut so that the final polished specimen represents the true microstructure. Examples include: silicon computer chips, gallium arsenide, brittle glasses, ceramic composites, and boron/graphite composites.
 |
 |
|
Fine grit diamond cut |
Medium grit diamond cut |
 |
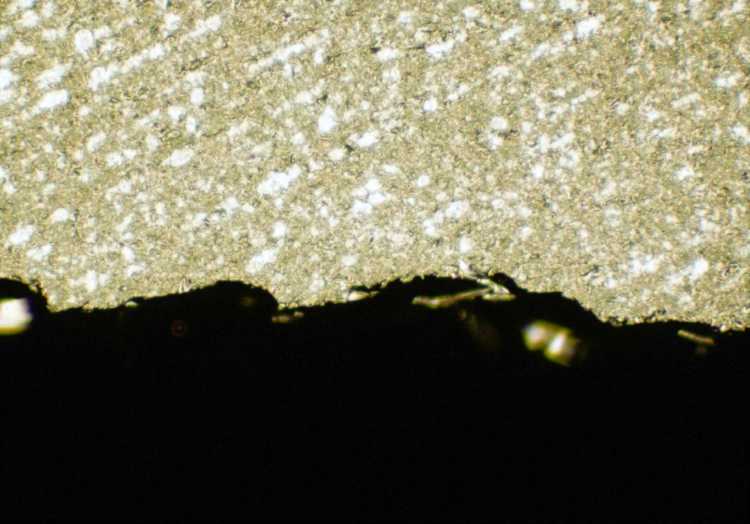 |
Fine grit diamond cut |
Medium grit diamond cut |
DIAMOND WAFER CUTTING PROCESS DESCRIPTION
Wafer Sectioning - Sectioning with diamond wafering blades is most commonly used for delicate materials requiring a precise cut. The important parameters for sectioning with wafering blades are speed, load, diamond concentration and diamond size. The cutting speed and applied loads are a function of the material being cut. Most common diamond wafering is done between 50 rpm and 5000 rpm with loads varying from 10-1000 grams. Generally, harder specimens are cut at higher loads and speeds (e.g. ceramics and minerals) and more brittle specimens are cut at lower loads and speeds (e.g. electronic silicon substrates).
Several factors are important for choosing the appropriate wafering blade. These include: diamond concentration (low and high), diamond bond (metal plate), diamond size (fine or medium), blade diameter and blade thickness. The diamond concentration is important because it directly affects the load which is applied during cutting. For example, brittle materials such as ceramics require higher effective loads to section, whereas ductile materials such as metals require more cutting points. The result is that low concentration blades are recommended for sectioning hard brittle materials such as ceramics and high concentration blades are recommended for ductile materials containing a large fraction of metal or plastic.
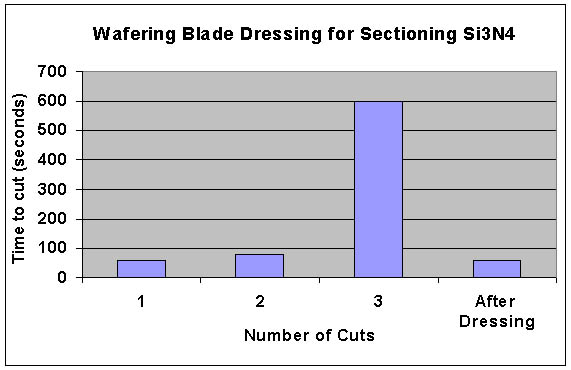
The diamond bonding material can also significantly affect a blades cutting performance. Metal plated wafering blades require periodic dressing to maintain performance. Contary to popular thought, cutting performance does not decrease because of the diamond being "pulled-out" of the blade. In reality, the metal bond is primarily smearing over the diamond and "blinding" the diamond abrasive. With periodic dressing this smeared material is removed and the cutting rate restored. The following graph shows this effect on very hard to cut material such as silicon nitride without dressing the blade. Following dressing the sample once again was cut in 30 seconds.
RECOMMENDED DIAMOND WAFERING PROCEDURES
- Condition the wafering blade with the appropriate dressing stick to remove previous cutting swarf and smeared metal from the wafering blade. A properly conditioned blade will cut faster and last longer. It is recommended that the dressing stick be mechanically applied to avoid twisting and chipping of the blade
- Clamp the specimen appropriately so that the sample does not shift during cutting
- For brittle materials clamp the specimen with a rubber pad to absorb vibration from the operation
- Begin the cut with a lower load to set the blade
- Orient the specimen so that the cut is through the smallest cross section
- Use largest appropriate blade flanges to prevent the blade from becoming distorted
- Reduce the load towards the end of the cut for brittle specimens (reduces fracturing at the end of the cut)
- Use the appropriate cutting fluid
Lubrication during abrasive cutting and diamond wafer cutting are required to minimize damage and to remove the cutting debris or swarf. For abrasive cutters the proper cutting fluid can have the added benefit of coating the cast iron bases and fixtures to eliminate corrosion and rusting of the cutter.
- Oil based diamond wafer cutting fluid - For diamond wafer cutting of metals an oil based cutting fluid is required to prevent the metal from coating the blade. Oil based cutting fluids therefore prolong the life and cutting efficiency of the diamond blade when cutting specimens requiring a high level of lubrication
- Water based diamond wafer cutting fluid - For ceramics, minerals, and composite type of samples a water based cutting fluid is recommended. Water based cutting fluids are easier to clean off the specimen, especially if the samples are porous.
DIAMOND WAFER TROUBLE SHOOTING
Symptom |
Cause |
Action |
Chipped or broken blade |
||
Excessive blade wobble |
||
Low cutting rates |
||
Excessive specimen damage or chipping |
||
Burr formation on specimen at end of cut |
DIAMOND WAFER PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
4" Diameter (102 mm) Wafering Blade, 1/2" (12.7 mm) Arbor |
|||||
Application |
Conc. |
Diamond |
Thickness |
Catalog |
|
Brittle materials (microelectronic materials, friable ceramics, minerals) |
Low |
Fine |
0.015" |
WB-0040LC |
|
Hard/tougher ceramics (Si3N4, ZrO2) |
Low |
Medium |
0.015" |
WB-0045LC |
|
Most metal samples |
High |
Medium |
0.015" |
WB-0045HC |
|
5" Diameter (127 mm) Wafering Blade, 1/2" (12.7 mm) Arbor |
|||||
Application |
Conc. |
Diamond size |
Thickness |
Catalog |
|
Brittle materials (microelectronic materials, friable ceramics, minerals) |
Low |
Fine |
0.015" |
WB-0050LC |
|
Hard/tougher ceramics (Si3N4, ZrO2) |
Low |
Medium |
0.015" |
WB-0055LC |
|
Most metal samples |
High |
Medium |
0.015" |
WB-0055HC |
|
6" Diameter (153 mm) Wafering Blade, 1/2" (12.7 mm) Arbor |
|||||
Application |
Conc. |
Diamond size |
Thickness |
Catalog |
|
Brittle materials (microelectronic materials, friable ceramics, minerals) |
Low |
Fine |
0.017" |
WB-0060LC |
|
Hard/tougher ceramics (Si3N4, ZrO2) |
Low |
Medium |
0.017" |
WB-0065LC |
|
Most metal samples |
High |
Medium |
0.017" |
WB-0065HC |
|
7" Diameter (178 mm) Wafering Blade, 1/2" (12.7 mm) Arbor |
|||||
Application |
Conc. |
Diamond size |
Thickness |
Catalog |
|
Brittle materials (microelectronic materials, friable ceramics, minerals) |
Low |
Fine |
0.017" |
WB-0070LC |
|
Hard/tougher ceramics (Si3N4, ZrO2) |
Low |
Medium |
0.017" |
WB-0075LC |
|
Most metal samples |
High |
Medium |
0.017" |
WB-0075HC |
|
CBN Wafering Blades, 1/2" (12.7 mm) Arbor |
|||||
Application |
Conc. |
Grit size |
Thickness |
Catalog |
|
4-inch CBN wafering blade (medium grit, high concentration |
High |
Medium |
0.015" |
WCBN-0045 |
|
5-inch CBN wafering blade (medium grit, high concentration |
High |
Medium |
0.015" |
WCBN-0055 |
|
6-inch CBN wafering blade (medium grit, high concentration |
High |
Medium |
0.017" |
WCBN-0065 |
|
7-inch CBN wafering blade (medium grit, high concentration |
High |
Medium |
0.017" |
WCBN-0075 |
|
CUTTING FLUID |
|||||
Description |
Quantity |
Catalog |
|||
DIACUT water-based wafer cutting fluid |
16 oz (0.47l) |
WL-3000-16 |
|||
| DIACUT oil-based wafer cutting fluid | 16 oz (0.47l) 32 oz (0.94l) |
OL-3000-16 OL-3000-32 |
|||
MISCELLANEOUS |
|||
Description |
Quantity |
Catalog |
|
DIACUT Dressing sticks (medium grit) |
each |
DRES-0050 |
|
Porometric mounting pads |
24/pkg. |
PAD-0010 |
|